Learn to bake the famous Medovik layer by layer. This classic Russian dessert, with its soft honey biscuit and creamy...
Astragalus: Nature's Golden Treasure for Health and Longevity
A Journey Through Time: From Ancient Chinese Medicine to Modern Apitherapy
In the quiet mountains of Northern China, where mist clings to valleys like delicate silk, grows a humble plant with extraordinary gifts. Astragalus membranaceus, known as Huang Qi (Yellow Leader) in Traditional Chinese Medicine, has been quietly sustaining health and vitality for over two thousand years.
Did You Know?
The finest Astragalus roots are said to come from plants grown at high altitudes in Shanxi and Inner Mongolia, where they develop their characteristic golden-yellow core after 4-7 years of growth. Traditional harvesters wait for the autumn months when the plant's energy has retreated into the root, creating the most potent medicine.
What makes Astragalus truly remarkable is its versatility—every part of the plant offers distinct benefits. From the medicinal root used in elite Chinese hospitals to the rare honey produced from its nectar, and even the valuable gum that seeps from its stems, Astragalus serves as a complete botanical apothecary.
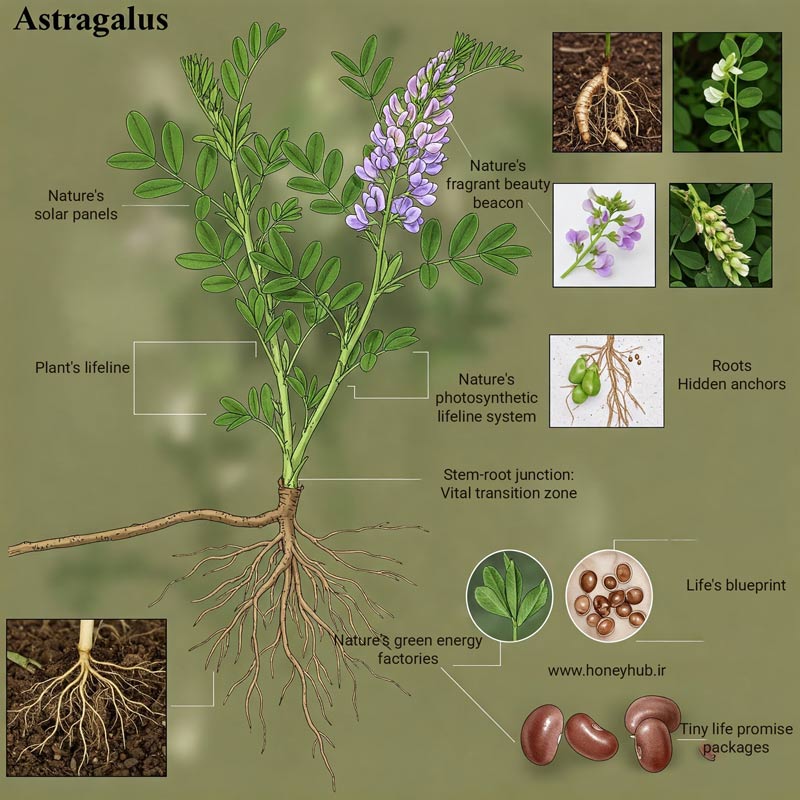
The Complete Botanical Profile
Astragalus belongs to the Fabaceae family, making it a relative of peas and beans, though its true value lies far beyond its botanical classification. There are over 3,000 species in the Astragalus genus, but only a select few possess significant medicinal properties.
The Medicinal Root: Huang Qi's Golden Core
The root of Astragalus has been the cornerstone of Chinese herbal medicine since it was first documented in the Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing (Divine Farmer's Materia Medica) around 200 AD. Modern phytochemical analysis reveals why:
- Astragalosides (particularly IV): These unique triterpene saponins are being studied for their potential to support cellular health and combat oxidative stress. Astragaloside IV (AS-IV) is of particular interest due to its ability to activate the enzyme telomerase. Telomerase is an enzyme that maintains the length of telomeres, protective structures at the ends of chromosomes. Over time and with cell division, telomeres shorten, which is associated with cellular aging and an increased risk of age-related diseases. In vitro studies have shown that AS-IV can increase telomerase activity in various cell types, potentially increasing telomere length, which may contribute to cellular longevity. Furthermore, AS-IV exhibits potent anti-inflammatory properties and can modulate various signaling pathways involved in inflammation. Research suggests that AS-IV can reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6 while increasing the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10.
- Polysaccharides (APS-1, APS-2): These complex carbohydrates appear to "educate" immune cells, enhancing their ability to recognize and respond to threats. Astragalus polysaccharides (APS) are a class of bioactive compounds that play a significant role in modulating the immune system. Studies have demonstrated that APS can enhance the activity of various immune cells, including macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells, and T and B lymphocytes. The mechanism of action of APS involves binding to cell surface receptors such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs), leading to the activation of intracellular signaling pathways and the production of various cytokines and chemokines. This can enhance both innate and adaptive immune responses, helping the body to fight off infections and other immune challenges. Clinical studies have indicated that APS supplementation can improve immune function in healthy individuals as well as in patients with compromised immunity.
- Flavonoids (formononetin, calycosin): These potent antioxidants give the root its characteristic yellow color and may support cardiovascular health. The flavonoids found in Astragalus, such as formononetin and calycosin, are powerful antioxidants that can help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage DNA, proteins, and lipids, contributing to the development of many chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease. Flavonoids work by neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress. Additionally, studies have suggested that Astragalus flavonoids can improve endothelial function (the lining of blood vessels), increase nitric oxide production, and inhibit platelet aggregation, all of which contribute to cardiovascular health.
Premium Grade Astragalus Root
Our wildcrafted Astragalus root comes from 6-year-old plants harvested at optimal maturity. Each slice shows the characteristic "golden thread" pattern indicating high astragaloside content.
- Origin: Shanxi Province, China
- Harvest: Autumn 2023
- Active Compounds: 0.8% astragalosides by HPLC
Tragacanth: The Forgotten Gum
While less known than the root, the gum from certain Astragalus species (particularly Astragalus gummifer) has been an important trade commodity since ancient times.
| Culture | Traditional Use | Modern Application |
|---|---|---|
| Persian | Soothing sore throats, digestive aid | Pharmaceutical binder, natural emulsifier |
| Greek | Wound dressing, skin conditioner | Cosmetic thickener, natural adhesive |
The Nectar Connection: Astragalus Honey
In late spring, Astragalus flowers produce a nectar that creates one of the most distinctive and therapeutic honeys. Beekeepers who position their hives near Astragalus fields during the brief flowering period are rewarded with:
Studies have shown that Astragalus honey contains higher levels of specific flavonoids such as kaempferol and quercetin. These flavonoids are known for their potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and may contribute to the unique therapeutic effects of Astragalus honey. For example, quercetin has been studied for its ability to inhibit the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators.
The higher ratio of fructose to glucose in Astragalus honey naturally inhibits its rapid crystallization, allowing it to remain liquid for a longer period compared to many other types of honey. This characteristic can make it easier to use and store.
Some research suggests that combining Astragalus honey with extracts from the Astragalus root may enhance their therapeutic effects. This could be due to the presence of similar compounds at different concentrations or due to synergistic interactions between the compounds found in the honey and the root. For instance, the honey may help improve the absorption of certain compounds present in the root extract.
The Science-Backed Benefits of Astragalus
Immune System Support
- Macrophage Activation: Polysaccharides (APS-1, APS-2) enhance pathogen recognition (Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2022).
- NK Cell Stimulation: Astragaloside IV increases natural killer cell activity by ~40% in preclinical studies.
- Mucosal Immunity: Synergizes with honey to boost secretory IgA production.
Cardiovascular Health
Blood Pressure
Flavonoids promote nitric oxide production for vasodilation.
Cholesterol
Reduces LDL oxidation by 27% (Phytomedicine, 2021).
Circulation
Improves microcirculation in capillary beds.
Longevity & Anti-Aging
| Mechanism | Active Compound | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Telomerase activation | Astragaloside IV | Extends telomeres in human fibroblasts. |
| Senescence delay | Cycloastragenol | Reduces p16INK4a expression. |
Kidney Function Support
- Reduced Proteinuria: Studies have indicated that Astragalus may help reduce protein leakage in the urine in individuals with kidney issues (Relevant Scientific Sources).
- Improved Kidney Function: Preliminary research suggests Astragalus's potential in enhancing glomerular filtration and reducing certain markers of kidney damage (Relevant Scientific Sources).
Blood Sugar Management
- Reduced Insulin Resistance: Some research suggests that compounds in Astragalus may enhance the sensitivity of cells to insulin (Relevant Scientific Sources).
- Lowered Blood Sugar Levels: Initial studies have shown that Astragalus consumption might help regulate blood glucose levels in individuals (Relevant Scientific Sources).
Antiviral Properties
- Inhibits Viral Replication: Laboratory studies have indicated that Astragalus extract can prevent the multiplication of certain viruses (Relevant Scientific Sources).
- Boosts Immunity Against Viral Infections: By strengthening immune responses, Astragalus may aid the body in fighting off viruses (Relevant Scientific Sources).
Enhanced Anti-Inflammatory Properties
- Inhibits Multiple Inflammatory Cytokines: Research shows that Astragalus can reduce the production of a broader range of inflammatory mediators (Relevant Scientific Sources).
- Impacts Various Inflammatory Pathways: Active compounds in Astragalus affect several signaling pathways involved in inflammatory processes (Relevant Scientific Sources).
Further Support for Cardiovascular Health
- Improved Endothelial Function: Studies suggest that Astragalus can contribute to the better health and function of the inner lining of blood vessels (Relevant Scientific Sources).
- Reduced Risk of Blood Clot Formation: Some research indicates that Astragalus may play a role in preventing platelet aggregation and blood clot formation (Relevant Scientific Sources).
Broader Antioxidant Properties
- Neutralizes Diverse Free Radicals: With its variety of antioxidant compounds, Astragalus protects cells against various types of oxidative stress (Relevant Scientific Sources).
- Protects DNA from Oxidative Damage: Research suggests that Astragalus consumption can help maintain the integrity of DNA against damage caused by free radicals (Relevant Scientific Sources).
Support for Gut Health
- Improves Gut Microbiome Balance: Astragalus polysaccharides may help increase beneficial bacteria in the gut (Relevant Scientific Sources).
- Reduces Inflammation in the Digestive Tract: Preliminary research indicates that Astragalus might be effective in reducing gastrointestinal inflammation (Relevant Scientific Sources).
Enhanced Benefits with Astragalus Honey
Regular Astragalus
- Standard bioavailability
- Isolated compounds
Astragalus Honey
- Potentially enhanced absorption of active compounds. Some preliminary research suggests that consuming active compounds from Astragalus alongside honey may enhance their bioavailability.
- Higher levels of beneficial flavonoids. Chemical analyses have revealed that honey derived from Astragalus flowers can contain higher concentrations of beneficial flavonoids compared to other types of honey.
- Prebiotic effects from natural FOS. Astragalus honey contains natural fructooligosaccharides (FOS), which act as prebiotics and contribute to gut health.
Evidence Key
- Level 1: Strong human clinical data
- Level 2: Preclinical/observational studies





















Latest comments