Does your mozzarella refuse to stretch or just burn? The secret is science. From "pasta filata" to the crucial role...
Royal Jelly: A Science-Backed Guide to Benefits, Dosage, and Side Effects (2025)
Royal Jelly: Benefits, Molecular Mechanisms, and a Practical Guide

🐝 Introduction: More Than a Food, It's a Biological Regulator
Royal Jelly (RJ) is a complex, bioactive substance produced by worker honeybees. It's not merely a source of nutrition; it acts as a powerful biological determinant that dictates the fate of a honeybee larva. Exclusive feeding with royal jelly transforms a female larva into a fertile queen with a lifespan of several years, while other larvae develop into worker bees with lifespans of just a few weeks. This fascinating phenomenon, known as caste polyphnism, makes royal jelly one of the most compelling subjects in biology and nutritional science.1
The dramatic difference in lifespan and physiology between a queen and a worker, despite sharing an identical genome, is due to the epigenetic effects of royal jelly. This means the substance controls gene expression without altering the DNA sequence itself.
Despite royal jelly's popular reputation as an "elixir of youth" or "superfood," the scientific community approaches it with cautious optimism. Its therapeutic potential has shown significant promise in laboratory (in vitro) and animal (in vivo) studies, and its clinical applications in humans are a growing area of research. In this article, we provide a balanced and comprehensive perspective, delving into its compounds, evidence-backed benefits, molecular mechanisms, and practical tips for its use.
🧪 The Chemical Anatomy of Royal Jelly
Royal jelly is a complex colloid of water, proteins, sugars, and lipids. But its true value lies in its minor, yet powerful, bioactive components.
Additionally, royal jelly contains B vitamins (especially pantothenic acid or vitamin B5), trace minerals, polyphenols, enzymes, and hormones like testosterone.2 Two families of molecules are recognized as the primary drivers of royal jelly's properties:
- Major Royal Jelly Proteins (MRJPs): A family of nine proteins, named MRJP1 through MRJP9. MRJP1, also known as Royalactin, is identified as the key factor responsible for queen differentiation.
- Unique Fatty Acids: The most important is 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid (10-HDA), an unsaturated fatty acid found exclusively in royal jelly. It serves as a quality marker for standardizing royal jelly products.
The Standardization Challenge
The chemical composition of royal jelly is highly variable, depending on factors like bee species, season, geography, and local flora.3 This lack of uniformity makes it a significant challenge for researchers to compare study results and establish a standard therapeutic dosage.
✨ Potential Benefits for Human Health
Pharmacological research has attributed a wide range of therapeutic properties to royal jelly, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-cancer, antimicrobial, libido-enhancing, and anti-aging activities.2 These properties are largely due to its bioactive compounds like flavonoids, proteins, peptides, and fatty acids, as well as other yet-to-be-identified components.2 Here are some of the documented therapeutic properties:
1. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects
Royal jelly is rich in phenolic compounds and flavonoids that can neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, which is a root cause of many chronic conditions like cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases.2 Studies have shown that royal jelly can inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6, helping to control chronic inflammation. This effect alone is significant, offering a potential counterbalance to the inflammatory pressures of a modern lifestyle.
2. Immune System Regulation (Immunomodulation)
Rather than simply boosting or suppressing the immune system, royal jelly appears to modulate it. It can enhance immune response in cases of immunodeficiency and help temper it in autoimmune diseases where the system is overactive. This property is attributed to its ability to regulate T-cell function and antibody production.7
3. Metabolic Health (Diabetes and Cholesterol)
Limited human studies suggest that royal jelly consumption may help improve insulin sensitivity and lower fasting blood glucose levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes.6 There is also evidence suggesting it can help lower total and LDL ("bad") cholesterol, which could be beneficial in preventing atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).8
4. Brain Health and Neuroprotective Effects
This is one of the most exciting areas of research. Royal jelly has demonstrated the potential to protect nerve cells. Animal studies have shown it can improve cognitive function and shield neurons from oxidative damage. Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds may play a role in reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.2
5. Skin Health and Collagen Production
Royal jelly is used both topically and orally to improve skin health. Studies have shown that its unique fatty acid, 10-HDA, can promote collagen production by skin fibroblasts.6 Collagen is the primary structural protein in the skin, and increasing its production helps improve elasticity and reduce wrinkles. Its antimicrobial properties may also be useful in treating acne.
It's crucial to emphasize that most of these benefits are in the preliminary stages of research. Royal jelly should not be considered a replacement for standard medical treatments.
⚙️ Decoding the Molecular Mechanisms
The power of royal jelly lies in its ability to influence cellular signaling pathways and regulate gene expression.
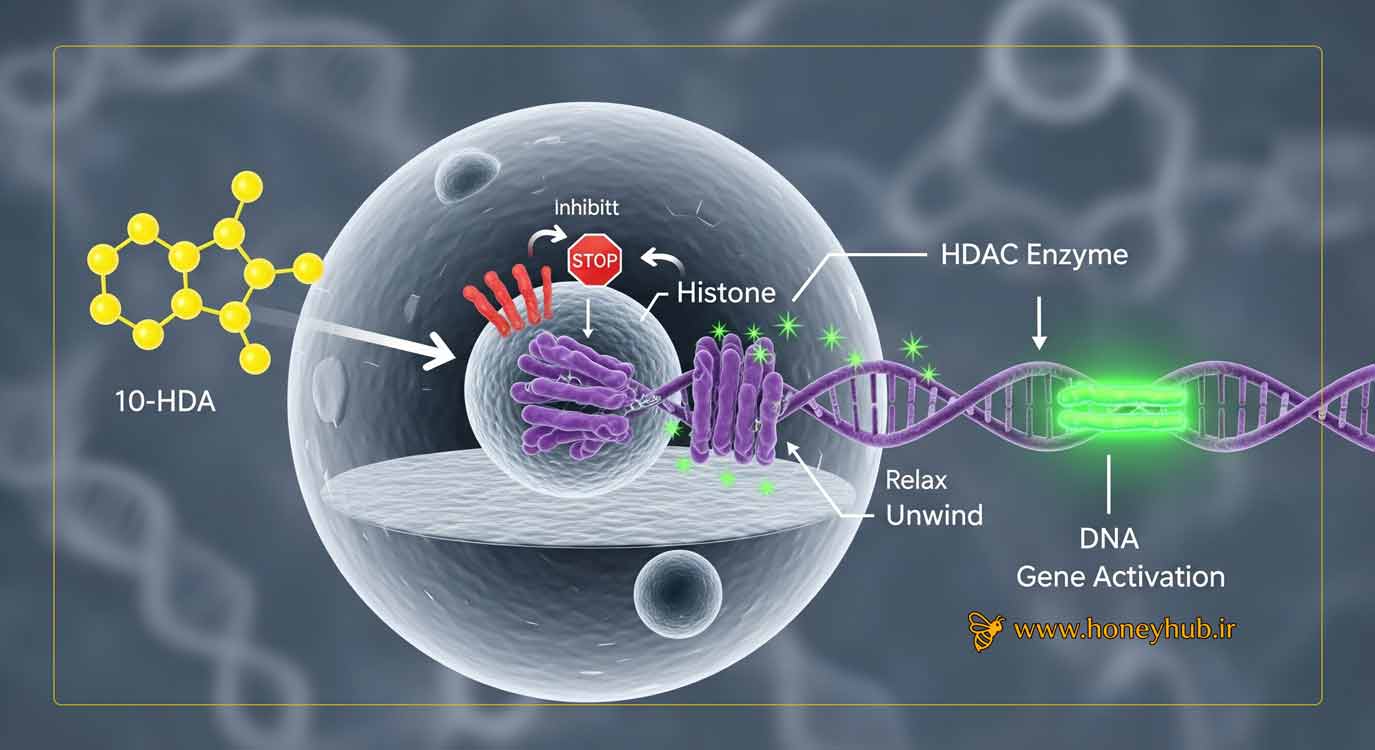
Epigenetics in Action: 10-HDA as an HDAC Inhibitor
One of the most fascinating discoveries is that 10-HDA acts as a Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor.10 Histones are proteins around which DNA is wound inside a cell. HDAC enzymes "silence" genes by keeping this structure tightly coiled and inaccessible. By inhibiting these enzymes, 10-HDA helps keep the DNA structure "open," allowing beneficial genes (like tumor suppressors or longevity-associated genes) to be expressed. This epigenetic mechanism is the foundation for many of royal jelly's purported anti-aging and anti-cancer properties.
Royalactin and the Activation of Growth Pathways
The protein MRJP1 (Royalactin) activates a cascade of cellular signals by binding to a receptor known as the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR).2 This signaling pathway also exists in humans and plays a key role in processes like cell growth, proliferation, and repair. This mechanism helps explain how royal jelly can contribute to tissue regeneration and cellular health.
🍯 Practical Guide: Use, Dosage, and Storage
Using royal jelly correctly is essential for reaping its benefits and avoiding potential side effects.
Forms and How to Use
Fresh Jelly: This is the most potent and bioactive form. Due to its sharp, acidic taste, it's typically taken sublingually (under the tongue for faster absorption) or mixed with a spoonful of honey.
Lyophilized (Freeze-Dried): This process removes water, increasing the product's stability. It's available in capsules or as a powder.
Topical Application: Creams and serums containing royal jelly are used for skin health.
Key Storage Tips
Fresh jelly must always be stored in the freezer.7 Its active compounds degrade quickly at refrigerator temperatures. For daily use, transfer a small amount to a separate container and keep it in the fridge, while the main supply remains frozen. Lyophilized products should be stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
Dosage Guide
The appropriate dose of royal jelly depends on age, health status, and the reason for use. The table below is a general guide, but consulting with a physician or nutritionist before starting is essential.7 Always begin with a low dose and gradually increase it.
| Group / Condition | Suggested Dose (grams/day) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Children (Over 5 years) | 0.5 g | For general wellness and appetite support (only with a doctor's approval). |
| Adults (General Wellness) | 1 to 3 g | For boosting energy, supporting immunity, and general health. |
| Adults (Therapeutic Goals) | 3 to 5 g | For specific conditions like menopause or metabolic support (under medical supervision). |
| Athletes & Recovery | Up to 10 g | For short periods to enhance recovery and reduce physical stress. |
⚠️ Safety and Precautions: What You Need to Know
This is the most critical warning: Individuals with asthma, eczema, or any allergy to bee products (honey, pollen, propolis, bee stings) should completely avoid royal jelly. Allergic reactions can range from mild hives to severe, life-threatening anaphylactic shock.6
Blood Thinners (e.g., Warfarin): Royal jelly may enhance the effect of these drugs, increasing the risk of bleeding.8
Blood Pressure Medications: Concurrent use might cause a significant drop in blood pressure.13
Diabetes Medications: It may potentiate the effects of blood sugar-lowering drugs, leading to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Always consult your doctor before use.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Due to a lack of sufficient safety data and potential hormonal effects, its use is not recommended during this time.8
Hormone-Sensitive Cancers: Because of its potential estrogen-like activity, individuals with a history of breast or prostate cancer should avoid it.
🔚 Final Conclusion
The Bottom Line
Royal jelly is a natural substance with extraordinary biological potential, its value extending far beyond its basic nutritional components. Its epigenetic mechanisms and influence on cellular signaling pathways are opening new frontiers in functional nutrition and preventive medicine. However, the science of royal jelly is still evolving. The excitement from lab results shouldn't blind us to the current limitations of human clinical data.
Royal Jelly Research Resources
Authoritative international references on the properties and applications of Royal Jelly.
The Effect of Royal Jelly on Cellular Lifespan
Investigating the molecular mechanisms of 10-HDA's effect on lifespan extension in animal models.
View PaperAnticancer Properties of Royal Jelly Compounds
A systematic review of the antitumor effects of Royalisin in gastrointestinal cancers.
View PaperGlobal Standards for Royal Jelly Production
A complete guide to extraction and storage methods for premium quality royal jelly.
View DocumentNeurological Applications of Royal Jelly
The effect of RJ compounds on improving cognitive function in Alzheimer's patients.
View StudyLeave a comment
Log in to post comments
Related posts
 Honey Hub, a treasure trove of nature's amazing products
Honey Hub, a treasure trove of nature's amazing products Why does pollen improve your health?
Why does pollen improve your health?



















Latest comments